No indexing means you’re invisible! Discover the game-changing steps to get your content indexed and dominate the search results.
Sick of seeing the error “Discovered – currently not indexed” in Google Search Console (GSC)? This frustrating issue often leaves website owners and SEO specialists feeling bewildered and unsure of how to resolve it effectively. The message indicates that while Google has discovered your page, it has not yet been indexed for search results, which can significantly impact your website’s visibility and traffic. Understanding the root causes of this error is crucial, as it may stem from various issues like low-quality content, insufficient internal linking, or even server errors. To gain clarity on how to address this problem, consider delving into specific strategies for improving your site’s indexability and making necessary adjustments to enhance your overall SEO performance.
Too much SEO effort is focused on ranking but many sites would benefit from looking one level up – to indexing.
Why you should care?
Because your content can’t compete until it’s indexed, it is crucial to ensure that search engines discover and evaluate it. Proper indexing is the gateway for your audience to find your valuable insights and unique offerings. When your content is finally recognized and listed by search engines, it opens up opportunities for higher visibility, more traffic, and ultimately, greater engagement with your audience, allowing you to effectively convey your message.
Whether you’re using a ranking system or retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), your content won’t have any effect if it’s not indexed.
This applies to where your content shows up – whether it’s on regular search results pages, AI-generated results, Discover, Shopping, News, Gemini, ChatGPT, or any future AI platforms.
If your content isn’t indexed, it won’t be seen, clicked on, or make any impact.
Sadly, indexing problems are quite common.
From my experience with different websites, about 9% of important deep content pages (like products, articles, and listings) do not get indexed by Google and Bing.
So, how do you make sure your deep content doesn’t just vanish into the void?
Follow these nine proven steps to accelerate the process and maximize your site’s visibility, ensuring that each strategy not only enhances your online presence but also engages your target audience effectively. By implementing these techniques, you will witness a significant boost in traffic and user interaction, ultimately leading to improved conversion rates and a stronger brand reputation.
Step 1: Audit your content for indexing issues
In Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools, submit a separate sitemap for each page type:
- One for products.
- One for articles.
- One for videos.
- And so on.
After submitting a sitemap, it may take a few days to appear in the Pages interface.
Use this interface to filter and analyze how much of your content has been excluded from indexing and, more importantly, the specific reasons why.
All indexing issues fall into three main categories:
- Poor SEO directives
- These issues stem from technical missteps, such as:
- Pages blocked by robots.txt.
- Incorrect canonical tags.
- Noindex directives.
- 404 errors.
- Or 301 redirects.
- The solution is straightforward: remove these pages from your sitemap.
- These issues stem from technical missteps, such as:
- Low content quality
- If submitted pages are showing soft 404 or content quality issues, first ensure all SEO-relevant content is rendered server-side.
- Once confirmed, focus on improving the content’s value – enhance the depth, relevance, and uniqueness of the page.
- Processing issues
- These are more complex and typically result in exclusions like “Discovered – currently not indexed” or “Crawled – currently not indexed.”
While the first two categories can often be resolved relatively quickly due to their straightforward nature and the clear guidelines available, processing issues demand more time and attention, as they often involve intricate layers of complexity that require thorough investigation and careful analysis. These issues might stem from unexpected variables or discrepancies that can significantly alter the outcomes, necessitating a more methodical approach to ensure that all aspects are considered before reaching a conclusion.
By using sitemap indexing data as benchmarks, you can track your progress in improving your site’s indexing performance.
Step 2: Submit a news sitemap for faster article indexing
For article indexing in Google, be sure to submit a News sitemap.
This specialized sitemap includes specific tags designed to speed up the indexing of articles published within the last 48 hours, ensuring that fresh content is promptly recognized by search engines. By utilizing these tailored tags, webmasters can enhance their site’s visibility and improve the chances of attracting new readers who are seeking the latest information. This approach not only fosters a dynamic user experience but also helps maintain your site’s relevance in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
Importantly, your content doesn’t need to be traditionally “newsy” to benefit from this submission method. In fact, this approach is versatile enough to accommodate various types of information and insights, allowing for a broader range of expression and creativity. Whether you are sharing personal stories, opinion pieces, or even specialized knowledge, utilizing this method can enhance the reach and engagement of your content. It opens the door for unique narratives that might not fit the conventional news format but still hold significant value for your audience. Embracing this flexibility can lead to more meaningful connections with readers who appreciate diverse perspectives and formats.
Step 3: Use Google Merchant Center feeds to improve product indexing
While this applies only to Google and specific categories, submitting your products to Google Merchant Center can significantly improve indexing.
Ensure your entire active product catalog is added and kept up to date.
Step 4: Submit an RSS feed to speed up crawling
Create an RSS feed that includes content published in the last 48 hours.
Submit this feed in the Sitemaps section of both Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools.
This works effectively because RSS feeds, by their nature, are crawled more frequently than traditional XML sitemaps.
Plus, indexers still respond to WebSub pings for RSS feeds – a protocol no longer supported for XML sitemaps.
To maximize benefits, ensure your development team integrates WebSub.
Step 5: Leverage indexing APIs for faster discovery
Integrate both IndexNow (unlimited), which provides a seamless way to notify search engines about changes to your website’s content, and the Google Indexing API (limited to 200 API calls per day unless you can secure a quota increase), allowing you to effectively manage and enhance how your URLs are indexed by Google. By employing both tools, you can maximize your site’s visibility, ensuring that your content is promptly recognized and indexed by search engines, which is crucial for maintaining your competitive edge in the ever-evolving digital landscape. These integrations not only streamline the process of keeping search engine crawlers informed but also provide insightful metrics that can help you fine-tune your SEO strategies for better performance and user engagement.
Officially, the Google Indexing API is only for pages with job posting or broadcast event markup, emphasizing its specialized use case for these types of content. This limitation ensures that the API is utilized effectively, as it allows search engines to index and display relevant job listings or event broadcasts more efficiently. By focusing solely on these specific page types, the Google Indexing API helps streamline the updating process of indexed content, ultimately improving the visibility of job opportunities and events in search results while providing a more targeted experience for users seeking such information.
(Note: The keyword “officially.” I’ll leave it to you to decide if you wish to test it.)
Step 6: Strengthen internal linking to boost indexing signals
Indexers primarily discover content through links, with URLs that have stronger link signals being prioritized in the crawl queue and possessing greater indexing power. Although external links are important, internal linking plays a crucial role in optimizing large sites with numerous deep content pages. Key areas for optimization include related content blocks, pagination, breadcrumbs, and links on the homepage, which enhance visibility for Googlebot and Bingbot.
When it comes to the homepage, you can’t link every deep content page – but you don’t need to. Instead, focus on showcasing the most important and relevant pages that capture the essence of your website, while providing clear navigation to guide users towards a more in-depth exploration of your offerings. By strategically selecting which pages to highlight, you can create a streamlined experience that prioritizes user engagement and leads visitors to key content without overwhelming them with choices. This approach not only enhances usability but also helps improve your site’s overall SEO by directing traffic to your most valuable resources.
Focus on those that are not yet indexed. Here’s how:
- When a new URL is published, check it against the log files.
- As soon as you see Googlebot crawl the URL for the first time, ping the Google Search Console Inspection API.
- If the response is “URL is unknown to Google,” “Crawled, not indexed,” or “Discovered, not indexed,” add the URL to a dedicated feed that populates a section on your homepage.
- Re-check the URL periodically. Once indexed, remove it from the homepage feed to maintain relevance and focus on other non-indexed content.
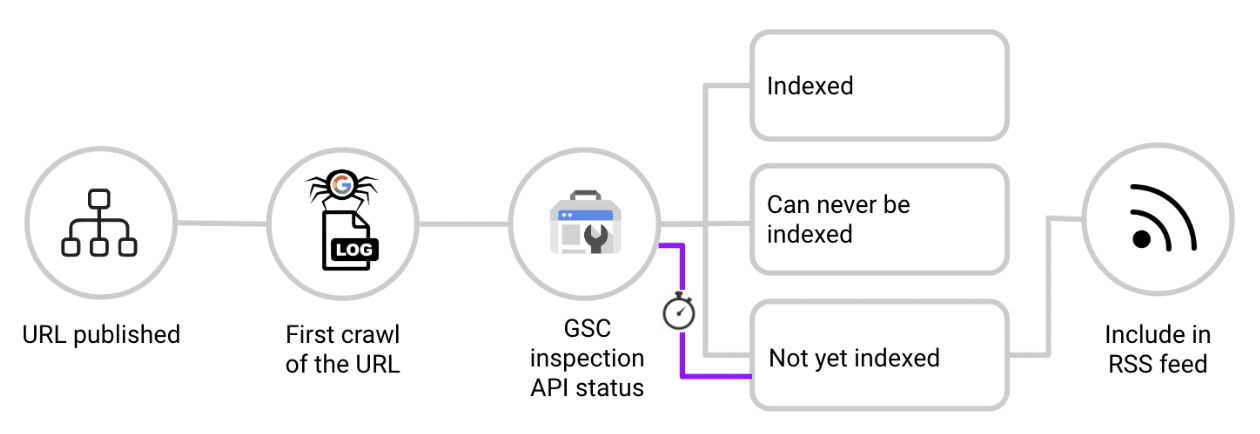
This effectively creates a real-time RSS feed of non-indexed content linked from the homepage, leveraging its authority to accelerate indexing.
Step 7: Block non-SEO relevant URLs from crawlers
Regularly audit log files and block high-crawl, low-value URLs with robots.txt disallow.
Pages such as faceted navigation, search result pages, tracking parameters, and other irrelevant content can:
- Distract crawlers.
- Create duplicate content.
- Split ranking signals.
- Ultimately downgrade the indexer’s view of your site quality.
However, a robots.txt disallow alone is not enough.
If these pages have internal links, traffic, or other ranking signals, indexers may still index them.
To stop this from happening, you have to take a stand now! Don’t let complacency be your downfall; it’s time to challenge the unacceptable and demand change. The clock is ticking, and sitting idly by will only deepen the crisis. It’s time to act, to disrupt the status quo, and to ignite a fire of transformation!
- In addition to disallowing the route in robots.txt, it is important to apply rel=”nofollow” to all possible links that point to these specific pages in order to prevent search engines from following them and to ensure that they do not pass any link equity or influence the site’s overall SEO performance.
- Ensure this is done not only on-site but also in transactional emails and other communication channels to prevent indexers from ever discovering the URL.
Step 8: Use 304 responses to help crawlers prioritize new content
For most websites, a lot of crawling time goes to checking and refreshing content that is already indexed.
When a site sends a 200 response code, it means that indexers will download the content again and compare it to what they already have.
This process is useful when content has been updated, but it’s not needed for most pages.
For pages that haven’t changed, it’s better to send a 304 HTTP response code (“Not Modified”).
This tells crawlers that the page remains the same, allowing indexers to focus on finding new content instead.
Step 9: Manually request indexing for hard-to-index pages
For URLs that don’t get indexed, manually submit them in Google Search Console.
Remember, you can only submit 10 URLs each day, so choose carefully.
In my experience, submitting manually in Bing Webmaster Tools isn’t better than using the IndexNow API.
So, using the API is a more efficient option.
Maximize your site’s visibility in Google and Bing
If your content isn’t indexed, it’s invisible. This means that even the most carefully crafted articles, blog posts, or web pages can go unnoticed by your target audience, limiting their reach and effectiveness. Don’t let valuable pages sit in limbo without the visibility they deserve.
One of the first steps in ensuring your content gets indexed is to understand the various factors that contribute to indexing. Search engines utilize algorithms that crawl and evaluate web pages based on several criteria. Prioritize the steps relevant to your content type; for instance, ensure you are using proper headings, meta descriptions, and alt text for images. These elements not only enhance user experience but also signal to search engines the significance of your content.
Additionally, take a proactive approach to indexing by submitting your sitemap to search engines. This allows them to discover and index your pages more efficiently. Regularly update your content and maintain a robust internal linking structure to guide search engine crawlers throughout your site, enhancing the likelihood that your pages will be indexed promptly.
By following these strategies, you can unlock the full potential of your content. Not only will your valuable information be visible, but it will also attract more traffic, engage your audience, and ultimately lead to greater success in your online endeavors. Investing time and effort into indexing is a crucial step in the journey from content creation to audience engagement.